meta data for this page
This is an old revision of the document!
Operations
All shapes (primitives or the results of operations) can be passed to special functions to perform logical operations, e.g. removing a hole from a board. In all cases, the operation returns the results, and never changes the original shapes.
Union
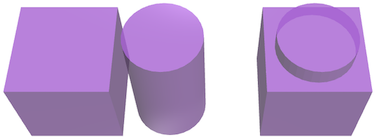
Several shapes can be combined (merged) into a single shape, creating complex 'parts'. The combining of smaller obects together allows the 'part' to be used in other operations, transformations, etc.
const newshape = union(cube({size: 10}), cylinder({radius: 4, heigth: 14})
Intersect

Several objects can be combined (overlapped) into a single shape. This result is the logical intersection of the shapes.
const newshape = intersect(cube({size: 10}), cylinder({radius: 4, heigth: 14})
Subtract

Several shapes can be removed (subtracted) from another. The result is the logical difference of shapes.
Note: The first shape given is the base shape for all subtractions.
const newshape = subtract(cube({size: 10}), cylinder({radius: 4, heigth: 14})
Hull

Several shapes can be combined together to form the convex hull, i.e. sum of the outside shells. This includes irregular shapes such as combining a circle with a square.
Learn more about convex hull at Wikipedia.org
const newshape = hull(shape1, shape2, shape3)
Hull Chain

Hull chain is a variant of 'hull' essentially sequential hulling each pair of shapes, then creating a union of the results.
const newshape = hullChain(shape1, shape2, shape3)

